- Vmware High Availability
- Vmware High Availability Definition
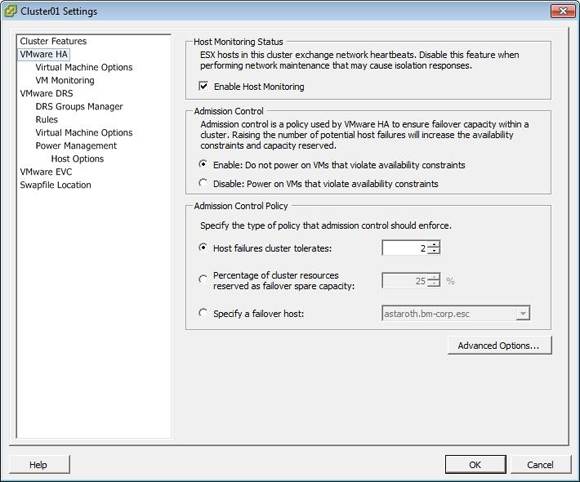
- Vmware High Availability Options
- Network Availability Calculation
- Vmware High Availability Best Practices
- Vmware High Availability Diagram
Dec 04, 2007 We get an enormous amount of questions about VMware’s HA (High Availability), especially when users see a message stating there are Insufficient resources to satisfy HA failover. We have already discussed the mechanism that HA uses to provide high availability here. Now we need to understand capacity calculations. Using the slot policy, vSphere HA performs admission control in the following way: Calculates the slot size. A slot is a logical representation of memory and CPU resources. By default, it is sized to satisfy the requirements for any powered-on virtual machine in the cluster. Determines how many slots each host in the cluster can hold.
| Print|Rate this content |
InformationThere are a lot of questions of how the slot calculation works. This document will help in understanding slot calculation with an example. DetailsAlthough the knowledge base article mentioned below, gives information on slot calculation but information given is restricted to a much generic information. Click here to view brief discription of slot calculation from VMware knowledge base . NOTE: The above-mentioned URL will take you to a non-HP Web site. HP does not control and is not responsible for information outside of the HP Web site. Slots are calculated by a combination of the total CPU and Memory that are in the physical hosts. The calculation for failover capacity works as follows: Example 1: Let us assume there are 4 ESX servers in the VMware HA cluster and Configured Failover capacity on the cluster is set to 1. Physical memory in the hosts is as follows:
In the cluster there are 24 VM’s each configured and running. Of the 24 VM’s running, determine the VM which has the highest 'configured memory'. For this example let’s say this is 2GB. All other VMs are configured with less or equal to 2GB. With this information the calculation can be now:
Example 2:
Why we need to understand slot calculation:
What logs do we need to check for slot calculation: Go to virtualcenter server 'C:Documents and SettingsAll UsersApplication DataVMwareVMware VirtualCenterLogsvpxd-x.log' open it with notepad and search for vpxdDas. This information applies to Virtual Center 2.x and 4.x |
Legal Disclaimer: Products sold prior to the November 1, 2015 separation of Hewlett-Packard Company into Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company and HP Inc. may have older product names and model numbers that differ from current models.
Provide feedback |
| Please rate the information on this page to help us improve our content. Thank you! |
- Was the information on this page helpful?
To ensure optimal vSphere HA cluster performance, you should follow certain best practices. This topic highlights some of the key best practices for a vSphere HA cluster. You can also refer to the vSphere High Availability Deployment Best Practices publication for further discussion.
When vSphere HA or Fault Tolerance take action to maintain availability, for example, a virtual machine failover, you can be notified about such changes. Configure alarms in vCenter Server to be triggered when these actions occur, and have alerts, such as emails, sent to a specified set of administrators.

Several default vSphere HA alarms are available.
Insufficient failover resources (a cluster alarm) | |
Cannot find master(a cluster alarm) | |
■ | Failover in progress(a cluster alarm) |
Host HA status(a host alarm) | |
■ | VM monitoring error(a virtual machine alarm) |
VM monitoring action (a virtual machine alarm) | |
■ | Failover failed (a virtual machine alarm) |
The default alarms include the feature name, vSphere HA.
A valid cluster is one in which the admission control policy has not been violated.
A cluster enabled for vSphere HA becomes invalid when the number of virtual machines powered on exceeds the failover requirements, that is, the current failover capacity is smaller than configured failover capacity. If admission control is disabled, clusters do not become invalid.
Vmware High Availability
In the vSphere Web Client, select vSphere HA from the cluster's Monitor tab and then select Configuration Issues. A list of current vSphere HA issues appears.
Vmware High Availability Definition
In the vSphere Client, the cluster's Summary tab displays a list of configuration issues for clusters. The list explains what has caused the cluster to become invalid or overcommitted.
DRS behavior is not affected if a cluster is red because of a vSphere HA issue.
In clusters where ESXi 5.x hosts and ESX/ESXi 4.1 or prior hosts are present and where Storage vMotion is used extensively or Storage DRS is enabled, do not deploy vSphere HA. vSphere HA might respond to a host failure by restarting a virtual machine on a host with an ESXi version different from the one on which the virtual machine was running before the failure. A problem can occur if, at the time of failure, the virtual machine was involved in a Storage vMotion action on an ESXi 5.x host, and vSphere HA restarts the virtual machine on a host with a version prior to ESXi 5.0. While the virtual machine might power on, any subsequent attempts at snapshot operations could corrupt the vdisk state and leave the virtual machine unusable.
Vmware High Availability Options
The following recommendations are best practices for vSphere HA admission control.
Network Availability Calculation

Vmware High Availability Best Practices
Select the Percentage of Cluster Resources Reserved admission control policy. This policy offers the most flexibility in terms of host and virtual machine sizing. When configuring this policy, choose a percentage for CPU and memory that reflects the number of host failures you want to support. For example, if you want vSphere HA to set aside resources for two host failures and have ten hosts of equal capacity in the cluster, then specify 20% (2/10). | |
Ensure that you size all cluster hosts equally. For the Host Failures Cluster Tolerates policy, an unbalanced cluster results in excess capacity being reserved to handle failures because vSphere HA reserves capacity for the largest hosts. For the Percentage of Cluster Resources Policy, an unbalanced cluster requires that you specify larger percentages than would otherwise be necessary to reserve enough capacity for the anticipated number of host failures. | |
■ | If you plan to use the Host Failures Cluster Tolerates policy, try to keep virtual machine sizing requirements similar across all configured virtual machines. This policy uses slot sizes to calculate the amount of capacity needed to reserve for each virtual machine. The slot size is based on the largest reserved memory and CPU needed for any virtual machine. When you mix virtual machines of different CPU and memory requirements, the slot size calculation defaults to the largest possible, which limits consolidation. |
If you plan to use the Specify Failover Hosts policy, decide how many host failures to support and then specify this number of hosts as failover hosts. If the cluster is unbalanced, the designated failover hosts should be at least the same size as the non-failover hosts in your cluster. This ensures that there is adequate capacity in case of failure. |
Vmware High Availability Diagram
You can use vSphere HA and Auto Deploy together to improve the availability of your virtual machines. Auto Deploy provisions hosts when they power up and you can also configure it to install the vSphere HA agent on such hosts during the boot process. See the Auto Deploy documentation included in vSphere Installation and Setup for details.